Rapid Prototyping: The Complete Guide for 2025

What Is Rapid Prototyping?
How the Rapid Prototyping Process Works
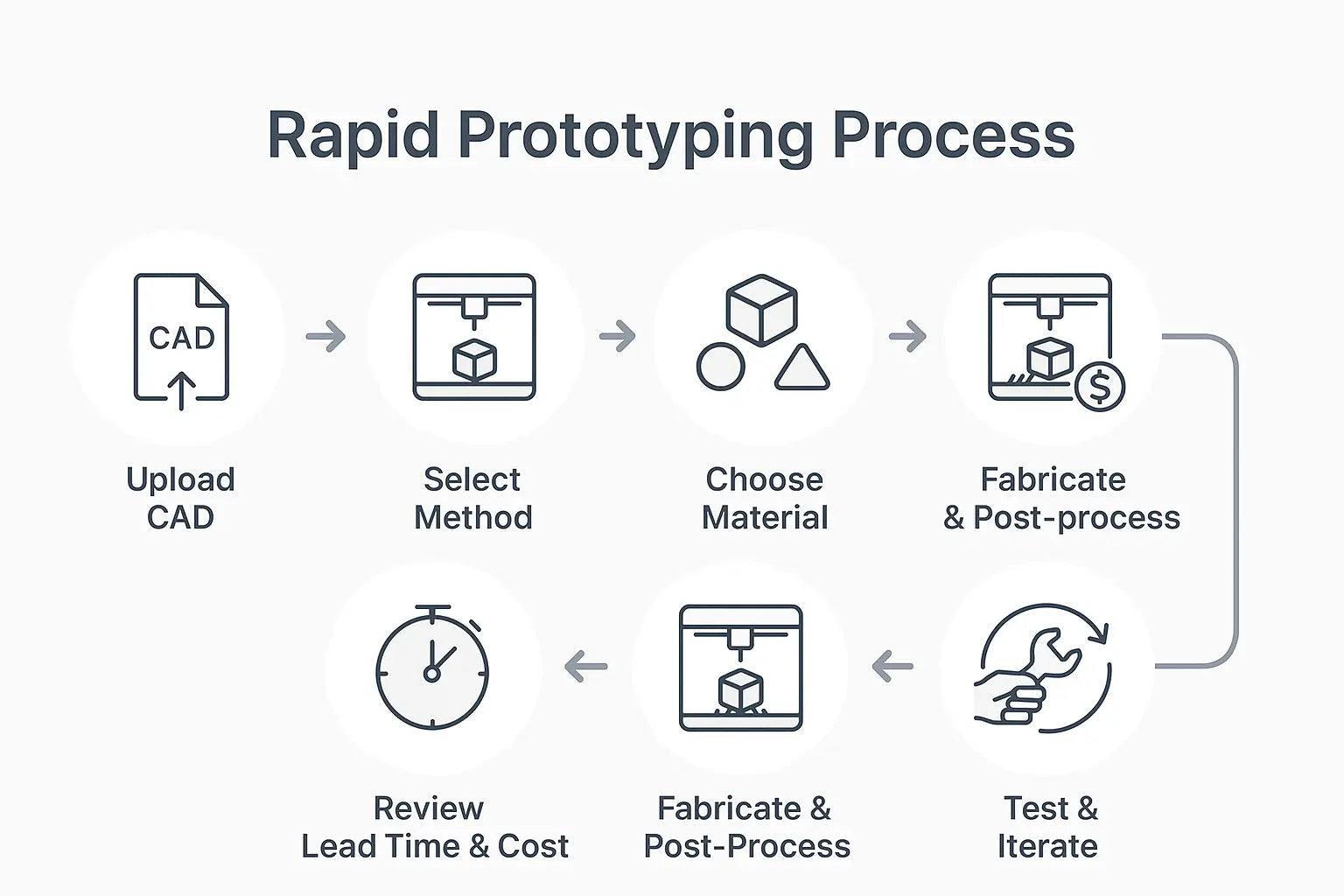
Step 1: Upload Your Design File
Step 2: Select the Right Prototyping Method
Step 3: Pick a Material That Matches Your Goals
Step 4: Review Lead Time & Cost
Step 5: Fabricate & Post-Process
Step 6: Test & Iterate
Common Types of Rapid Prototypes
🔹 Proof-of-Concept (PoC) Models
🔹 Looks-Like Prototypes
🔹 Works-Like Prototypes
🔹 Engineering Prototypes
🔹 Validation & Compliance Prototypes
3D Printing Technologies Used in Rapid Prototyping

SLA – High Detail for Visual Validation
SLS – Tough Functional Nylon Parts
FDM – Cost-Efficient Concept Models
Rapid Prototyping Materials: Plastic & Silicone
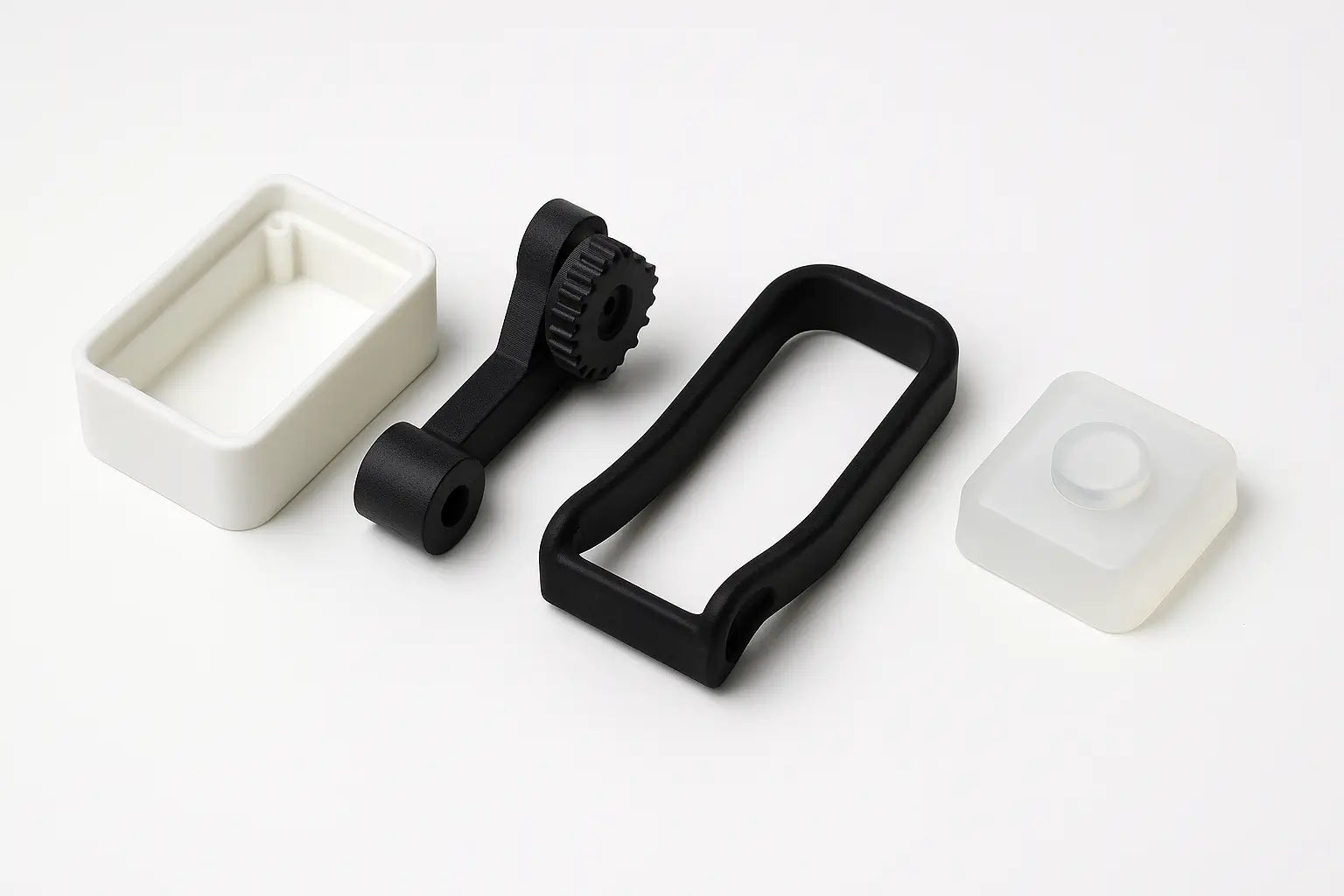

🔹 Standard Plastics (ABS-like Resins, PLA, ASA)
🔹 Engineering-Grade Nylon (PA11, PA12)
🔹 Flexible Materials (TPU, TPE)
🔹 Silicone for Urethane Casting
Key Applications of Rapid Prototyping by Industry
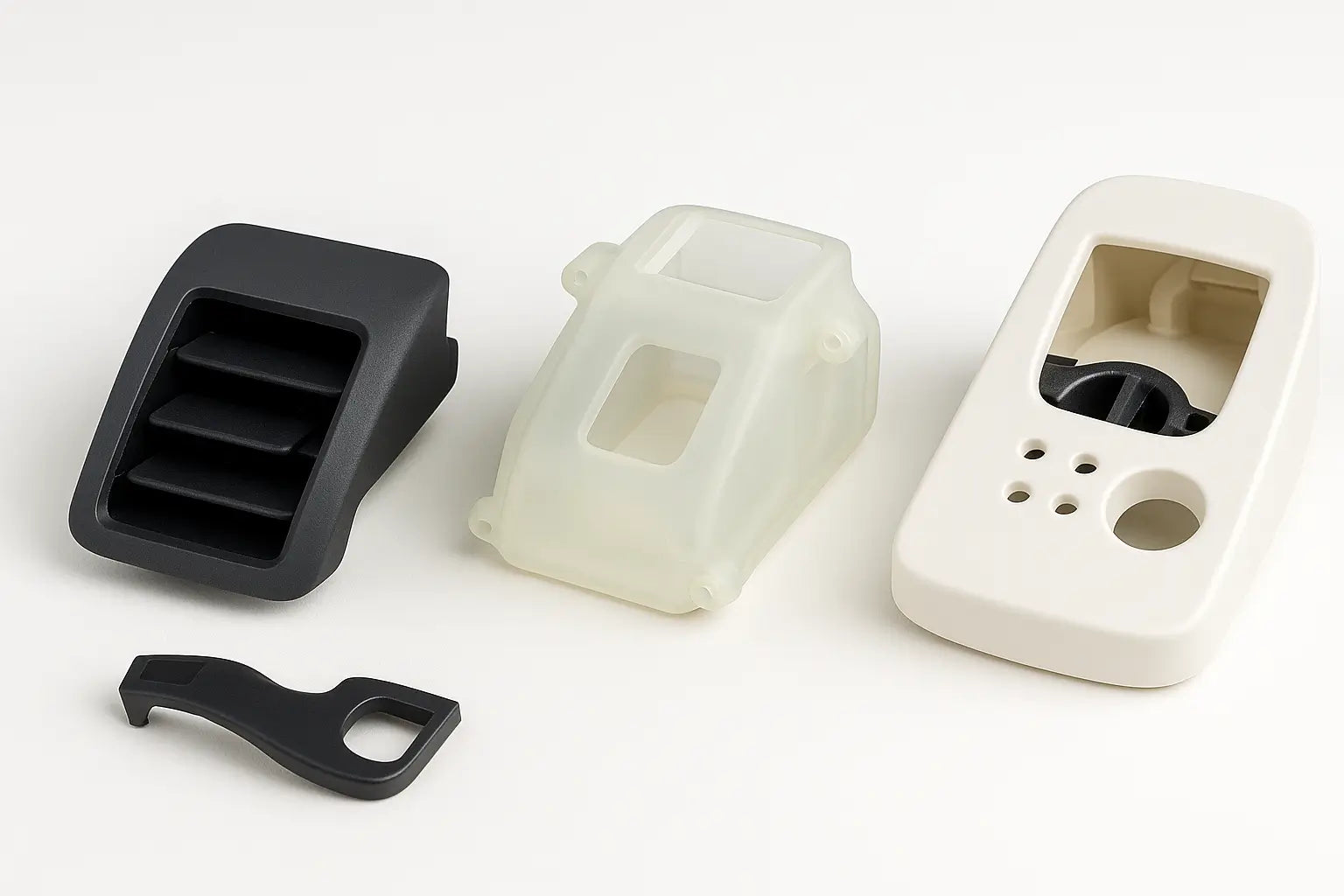

Automotive – From Dashboard Clips to Functional Under-the-Hood Components
Medical – Surgical Tools, Housings, and Regulatory Prototypes
Consumer Products – Iterate Before You Invest
Benefits of Rapid Prototyping
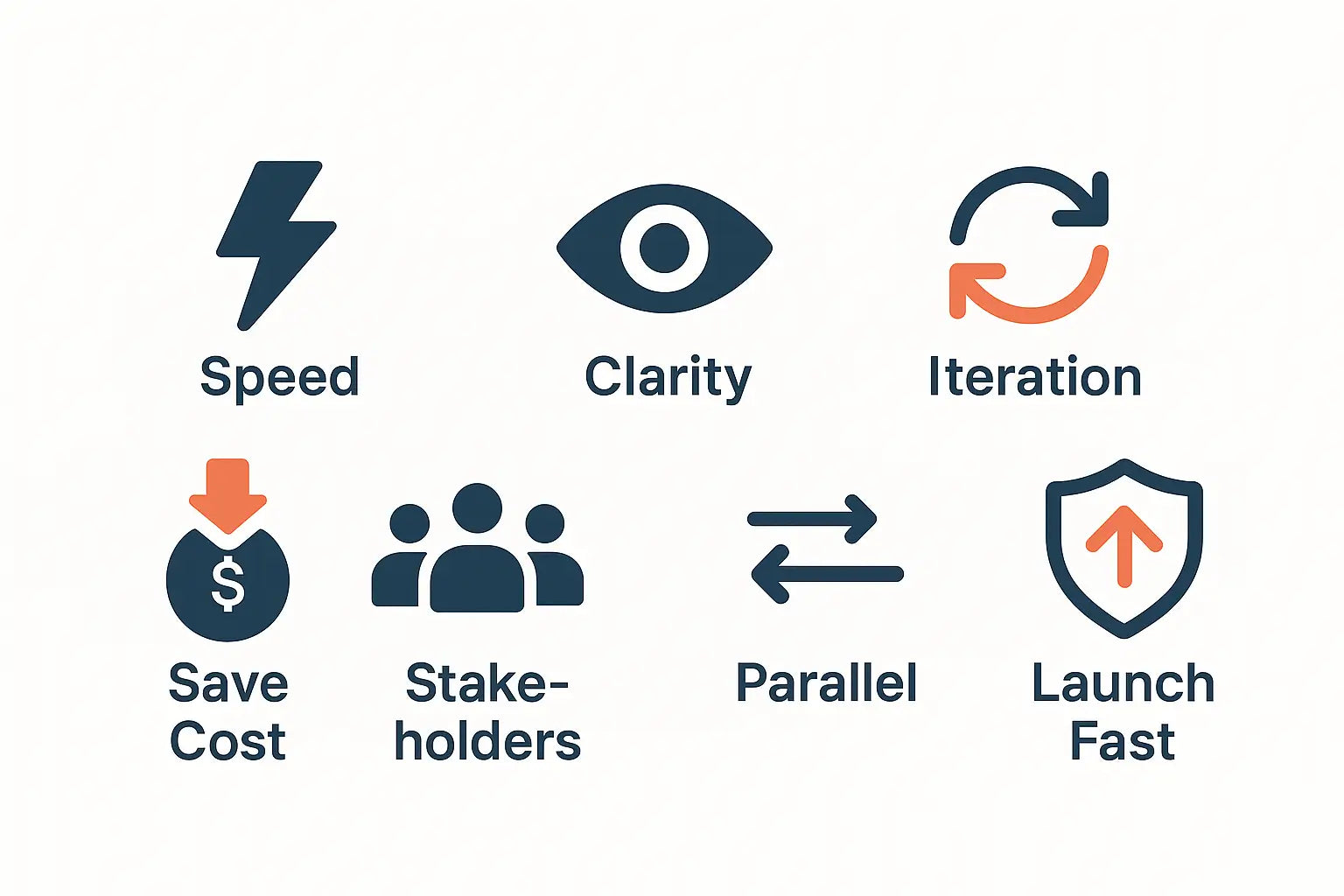
🔹 1. Fast Iterations = Faster Decisions
🔹 2. Visual & Functional Clarity
🔹 3. Fail Early, Learn Fast
🔹 4. Avoid the $10,000 Tooling Trap
🔹 5. Engage Stakeholders at Every Stage
🔹 6. Enable Parallel Workflows
🔹 7. Lower Risk, Higher Market Readiness
How to Choose the Right Process

Real Case Results
Automotive – From Missed Deadlines to Ahead of Schedule
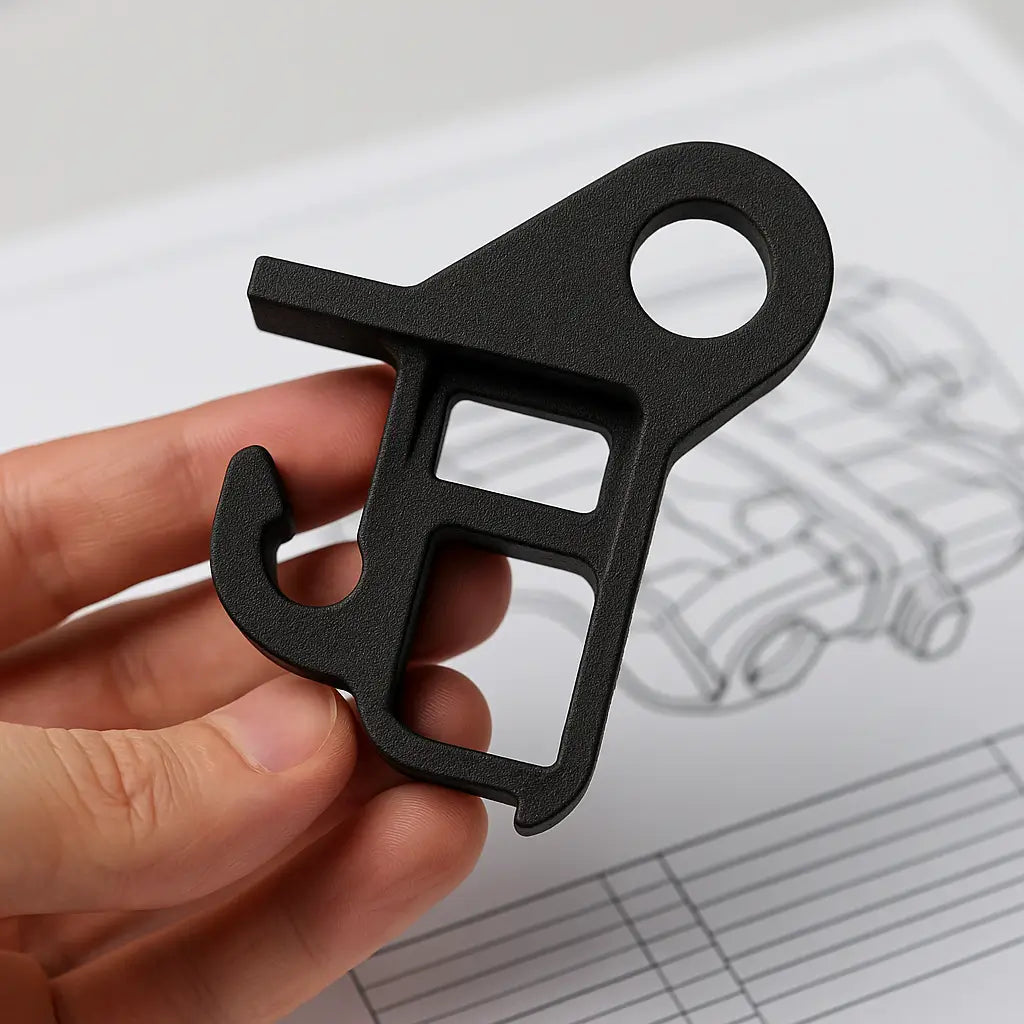

Medical – Getting Regulatory-Ready, Faster

Consumer Products – Scaling Feedback with Silicone Casting

