3D Printed Shoes: Complete Guide & Trends 2025

What Are 3D Printed Shoes?
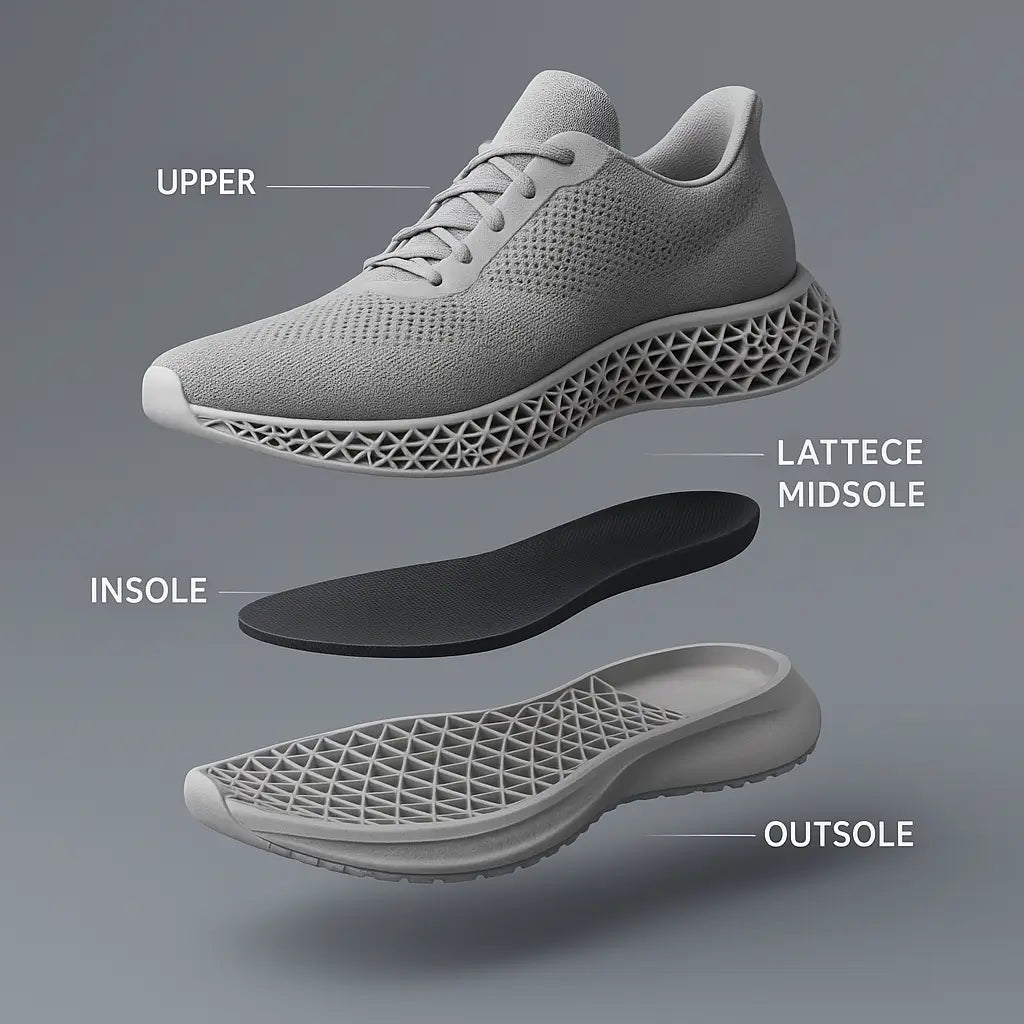

How Are They Printed?
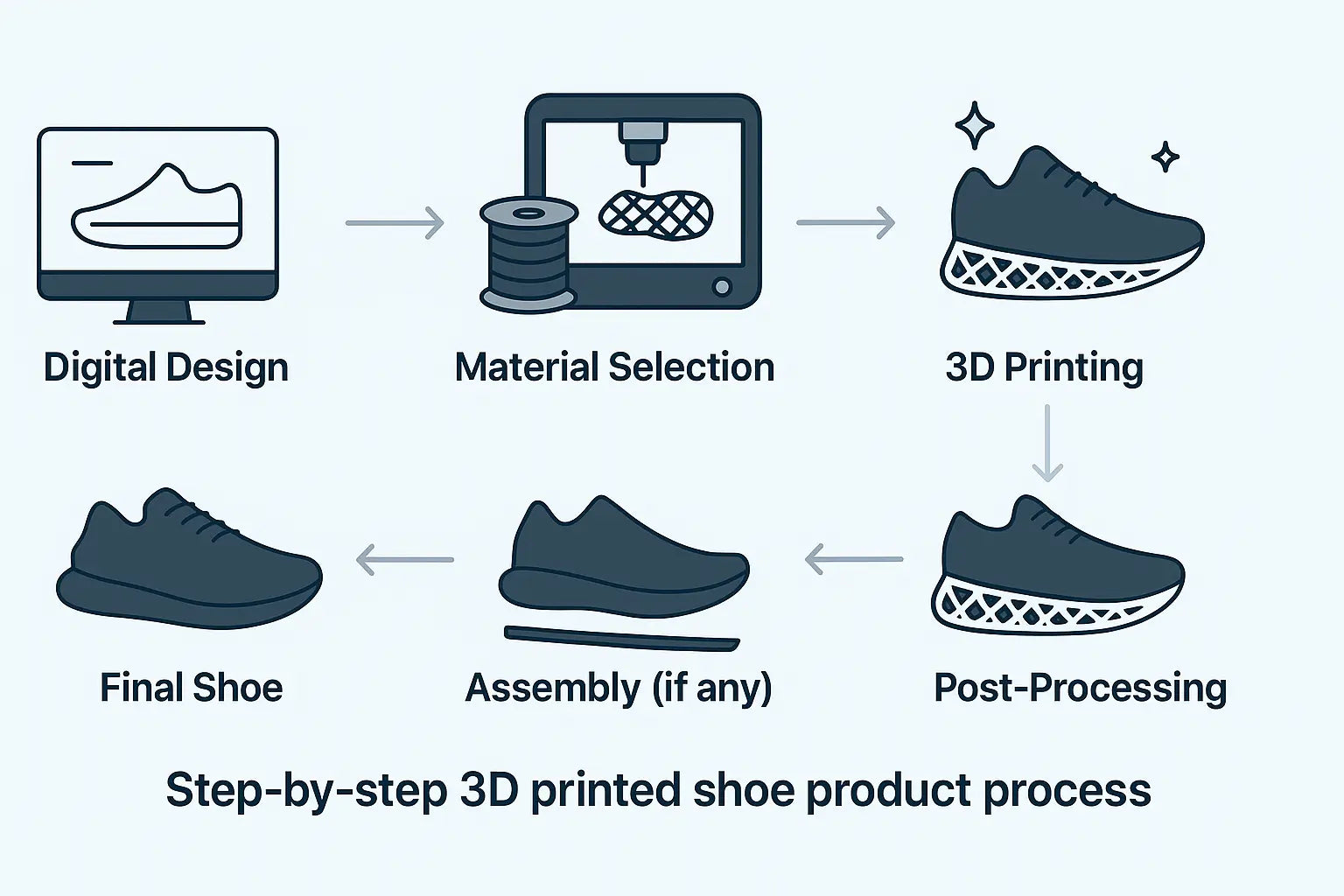

3D Printed Shoes Materials and Their Applications

Top 5 3D Printed Shoe Brands
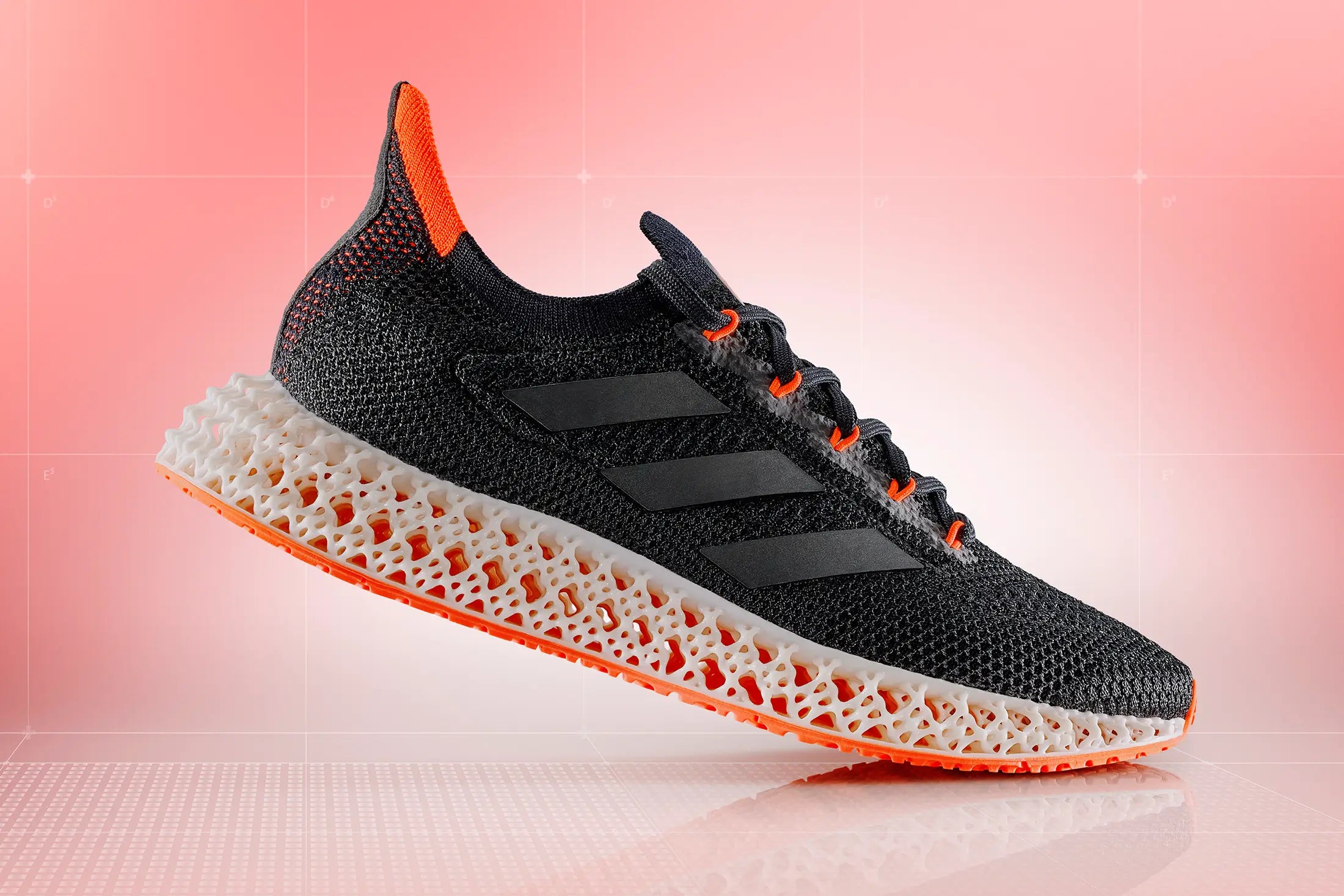

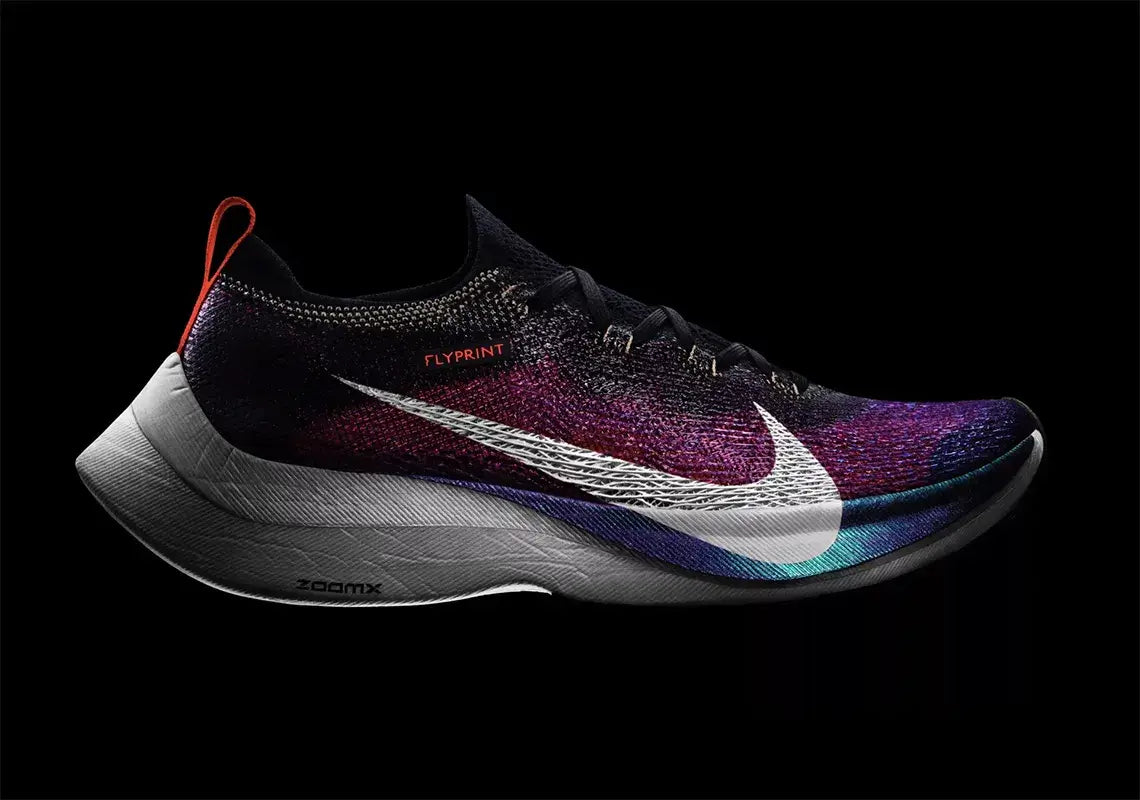
2. Nike — The Experimental Trailblazer

3. Zellerfeld

4. New Balance – The Precision Fit Specialist

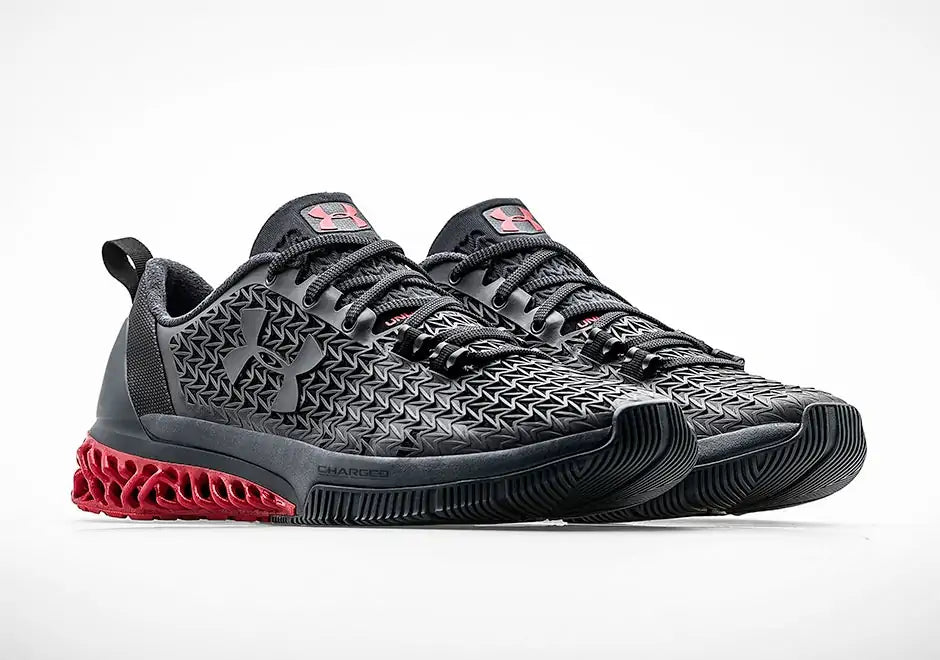
5. Under Armour – The Lattice Pioneer

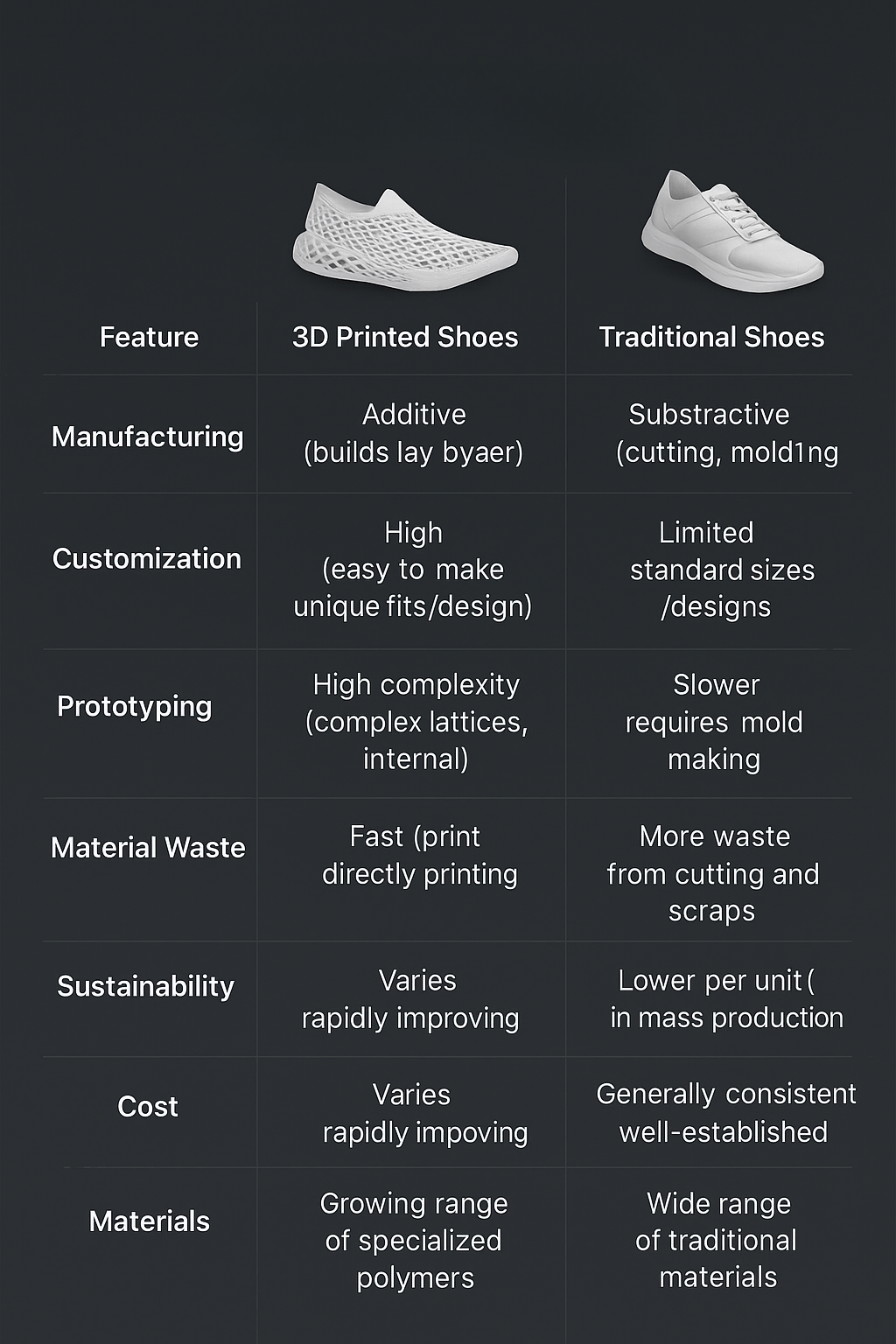
3D Printed Shoes vs. Traditional Shoes
Benefits of 3D Printed Shoes
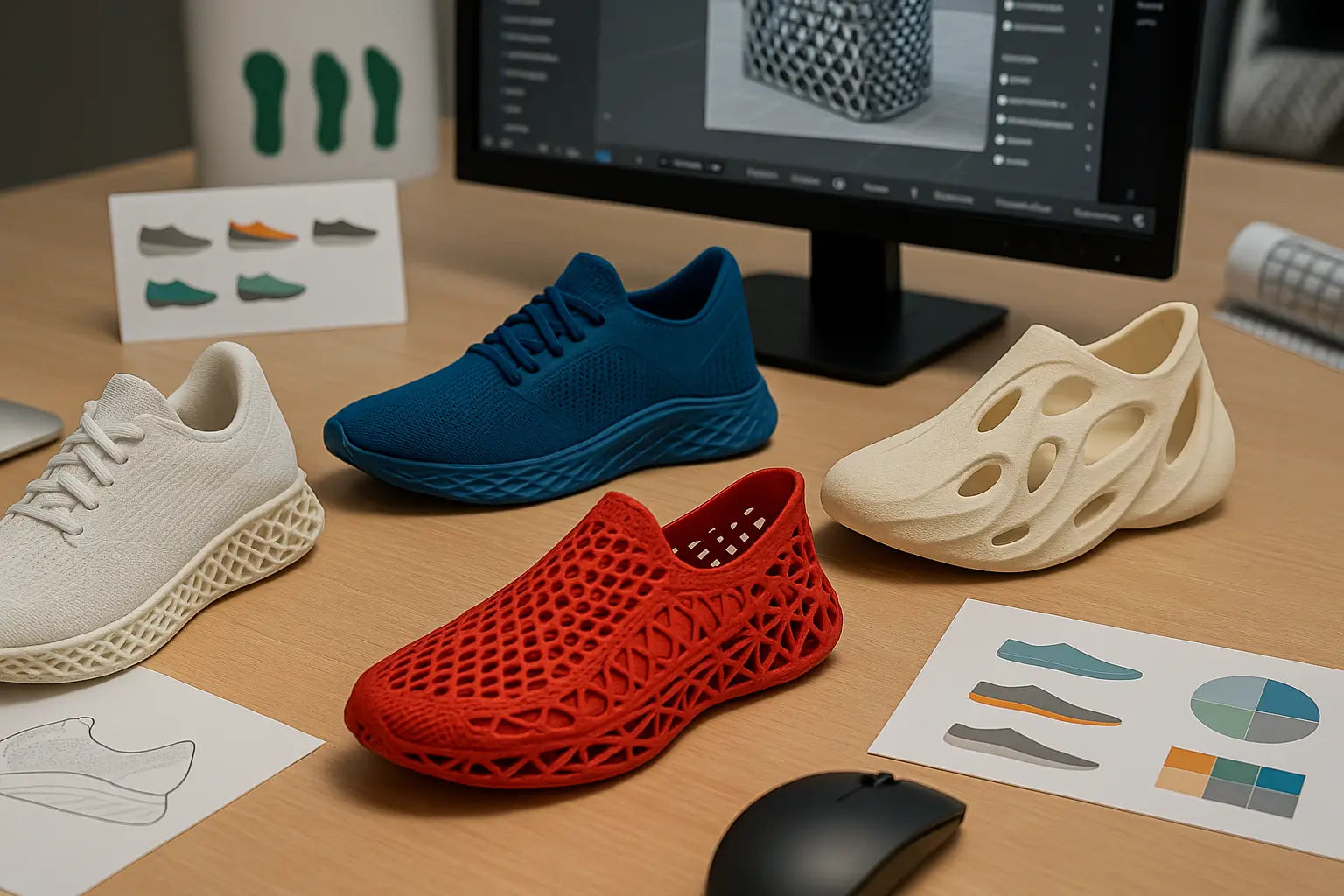

Unmatched Customization
Limitless Design Freedom
Rapid Prototyping
On-Demand Manufacturing
Sustainability Potential
Enhanced Performance
Local Production
Drawbacks and Challenges

Higher Costs
Durability Concerns
Material Limitations
Scalability Challenges
Technical Skill Barrier
Post-processing
Early Comfort Issues (Largely Overcome)
How Sustainable Are 3D Printed Shoes?
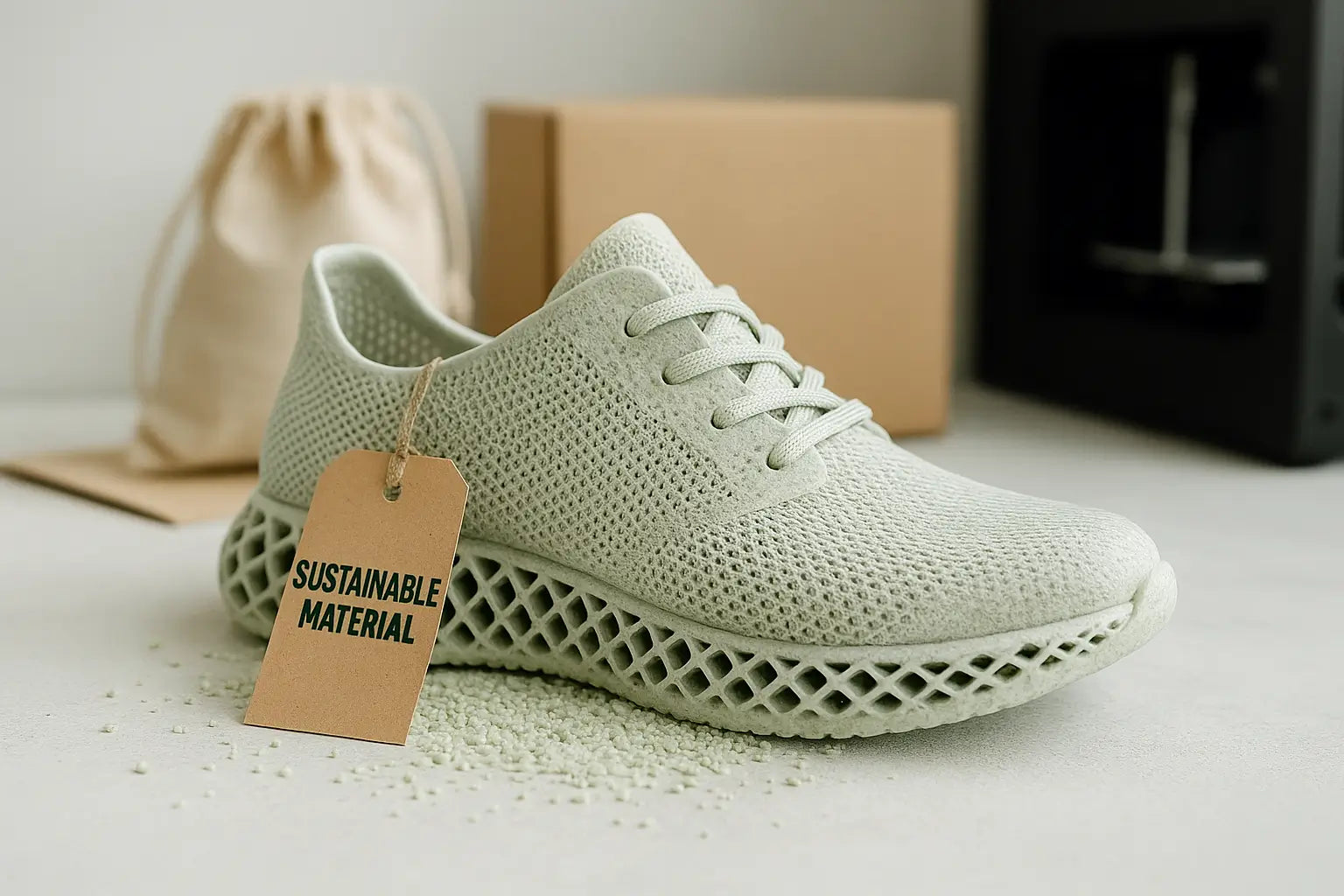

How 3D Printed Shoes Support Sustainability
Less Material Waste
Eco-Friendly Materials
Lower Carbon Emissions
Overall Environmental Impact
What’s Next for 3D Printed Shoes?

Mass Customization Goes Mainstream
Smarter, Stronger Materials
AI-Powered Design
Hybrid Manufacturing Takes Over
Local, On-Demand Printing
Rise of Smart Footwear
Built for Circularity
Athlete-Grade Performance Tuning
Bold New Design Possibilities
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
